|
| Driver’s Side Fuse Box Diagram Of Hyundai Santa Fe 2010 |
Saturday, September 20, 2014
Driver’s Side Fuse Box Diagram Of Hyundai Santa Fe 2010
25W Class A Power Audio Amplifier Wiring diagram Schematic
- The supply voltage must be a maximum of ±25V. This supply is simply obtained from a 20-0-20V transformer, recommended current is 1A.
- All resistors ought to be 1/4W or 1/2W 1% metal film for lowest noise, with the exception of R9, R10 and R15 which ought to be 1/2W varieties, and R13, R14 have to be 5W wirewound.
- Using the suggested and advised 25V supplies, Q4 will typically not need a heatsink. The output drivers (Q5 and Q6) recommended to use a heatsink, even though it doesn’t have to be big.
Fuse Box F250 2008 Ford Superduty 4WD Diagram
Fuse Box F250 2008 Ford Superduty 4WD Diagram
Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: blower motor relay, low to hi relay, heated mirror, A/C clutch relay, PCM power relay, starter relay, trailer tow relay, park lamp, trailer tow relay battery charger, run start relay, fuel pump motor diode, A/C clutch diode, stoplamp, trailer tow relay, reversing lamp relay, fuel pump relay.
Friday, September 19, 2014
TDA2040 20W HI FI Audio Amplifier
Here the hi-fi power amplifier schema which will deliver 20W power output. This amplifier schema use single power IC TDA2040 and a few external components.
Detailed explanation about this 20W Power Amplifier
Fuse Box Ford 2006 SUV Diagram
Fuse Box Ford 2006 SUV Diagram
Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: trailer tow park lamp, park lamp, ignition switch, powertrain control module, fuel pump relay, main fan relay, passive anti theft system, high mounnted stop lamp, stop lamp, powertrain control module, brake pedal position switch, instrument cluster, diagnostic connector, power mirror switch, audio unit, canister vant, power seats, sunroof, compass, radio, power window, suwoofer, low eams, horn.
Simple Video Amplifier
The video amplifier in the diagram is a well-known design. Simple, yet very useful, were it not for the ease with which the transistors can be damaged if the potentiometers (black level and signal amplitude) are in their extreme position. Fortunately, this can be obviated by the addition of two resistors.
Circuit diagram :
 Simple Video Amplifier Circuit Diagram
Simple Video Amplifier Circuit Diagram
If in the diagram R 3 and R 4 were direct connections, as in the original design, and P 1 were fully clockwise and P 2 fully anticlockwise, such a large base current would flow through T 1 that this transistor would give up the ghost. Moreover, with the wiper of P 2 at earth level, the base current of T 2 would be dangerously high. Resistors R 3 and R 4 are sufficient protection against such mishaps, since they limit the base currents to a level of not more than 5 mA.
Shunt capacitor C 4 prevents R 4 having an adverse effect on the amplification.
Automatic Night Light Feeds Directly From the AC Line
(Figure 1).

The schema uses inexpensive, off-the-shelf components, including the VT90N1 photoresistor; a 0.1-μF, 275V capacitor; and an L2004F61 TRIAC with a load current of 4A rms, a peak blocking voltage of 200V, and a gate-trigger current of 5 mA. The exact specifications of these components are not critical; you could use others instead.
Editor’s note:
Attributes worth mentioning include the fact that the capacitor introduces a phase shift, which places the peak of the gate voltage close to the zero crossing of the load’s sine wave for optimum turn-on timing. Another benefit is thermal hysteresis, which occurs due to the reduction of the required triggering voltage and current as the TRIAC warms up after the initial turn-on.
Thursday, September 18, 2014
4 x 12 W power amplifier with dynamic distortion detector and diagnostic interface
Requires very few external components
High output power
Fixed gain
Diagnostic facility (distortion, short-circuit and temperature detection)
Good ripple rejection
Mode select switch (operating, mute and stand-by)
Load dump protection
AC and DC short-circuit safe to ground and to VP
Low power dissipation in any short-circuit condition
Thermally protected
Reverse polarity safe
Electrostatic discharge protection
No switch-on/switch-off plop
Flexible leads
Low thermal resistance
Identical inputs.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8562Q is an integrated class-B output amplifier in a 17-lead single-in-line (SIL) power package. It contains 4 × 12 W single-ended amplifiers.
Circuit Diagram
 |
| 4 x 12 W power amplifier with dynamic distortion detector and diagnostic interface |
Fuse Box Ford 1989 Ranger Two Wheel Drive Diagram
Fuse Box Ford 1989 Ranger Two Wheel Drive Diagram
Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: headlamp, park horn, marker and turn signal, posiion battery cable, starter relay, cutout relay, distribution box, power relay, pump relay, test connection, power convenience group.
5V Power Supply Using LTM8021
5V Power Supply Circuit diagram

Wednesday, September 17, 2014
SONY KLV 32S550A KLV 26S550A – HOW TO DISASSEMBLE – LED BLINKING CODES







Fuse Box BMW Cibie CSR Diagram
Fuse Box BMW Cibie CSR Diagram


Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: high beam relay, low beam relay, auxiliary fan, turn signal, windshield wiper/washer, intensive cleaner, brake light, cruise control, horn, engine electrical equipment, back up light, fuel pump, check control, instrument cluster, on board computer, heater blower, back up light, outside power mirror, mirror heating, air conditioner, power seat memory, rear window defogger, interior light, glove box, memory, rechargable flash light, hazard warning light, engine compartment light, license plate light, power antenna, parked car heater, fog light.
Tuesday, September 16, 2014
Fuse Box Ford 2005 Freestyle Diagram
Fuse Box BMW R1150GS Diagram
Fuse Box BMW R1150GS Diagram

Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: flasher unit, dial needle damping, coding plug motronic, starter relay, load relief relay, horn relay, fuel pump relay, motronic relay, ABS warning system.
Explanation Fuse Box Chevy s10 2001 Diagram
Fuse Box Chevy s10 2001 Diagram


Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: back up lamp, supply voltage, trailer rear, stop lamp supply, back lamp supply, park lamps supply voltage, trailer CHMSL supply voltage, fuel pump supply, ignition voltage.
Monday, September 15, 2014
Noise Suppression For R C Receivers



Signals with frequencies close to the 10.4-MHz intermediate frequency (which is used in many receivers) are also effectively blocked by this filter. L9 filters out common-mode noise on the supply line for the servos, which effectively means that it prevents the supply lines to the servos from acting as antennas. Finally, high-frequency currents on the servo signals are filtered out by ferrite beads in order to limit the antenna effects of these connection lines.
Resistor:
- R1 = 1Ω
- C1 = 100nF
- C2 = 22pF
- L1-L8,L10 = ferrite inductor
- L9 = common-mode coil
- K1-K8 = servo cable
- K9-K17 = 3-way SIL pinheader
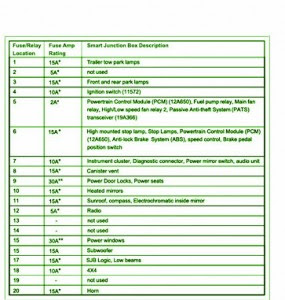
Mercedes Explanation Fuse Box Year Benz 1995 C280 Diagram
Fuse Box Mercedes Benz 1995 C280 Diagram

Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: heater relay module, ASR charging pump relay module, A/R relay module, auxiliary relay fan module, HCS realay module, horn relay module, daytime running lamp, return pump relay, combination relay, hazard signal, heated rear window, wiper motor, exterior lamp failure monitoring module.
Relay Based Motorcycle Alarm Wiring diagram Schematics

Relay coils and some sounders produce high reverse-voltage spikes that will destroy sensitive electronic components. D1 and D2 are there to short-schema these spikes before they can do any damage. Although there is nothing in the alarm schema itself that could be damaged - I have no idea what other electronic equipment might be connected to the same power supply. So I included the two diodes as a precaution. If youre satisfied that theres nothing on your bike that might be damaged in this way - you can leave out the two diodes.
Relay Based Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram 2 uses a DPCO/DPDT relay - but you really only need to use a DPST relay. If you are going to use the veroboard layout provided - youll need to use the style of relay specified. But you can build the alarm using whatever style of relay you have available.
Relay Based Motorcycle Alarm Circuit Diagram 2
Sunday, September 14, 2014
Explanation Fuse Box Chevrolet ZR2 2003 Diagram
Fuse Box Chevrolet ZR2 2003 Diagram
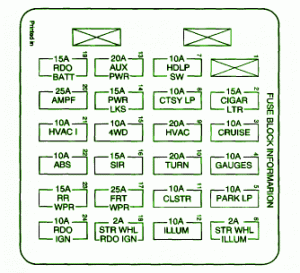

Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: cigar lighter, data link connector, body control module, cruise control module, multifunction switch, driver front passenger, instrument panel cluster, view mirror switch, door lock, side window lock out switch, audio control, IP ashtray lamp, redundant steering wheel control, headlamp switch, seat lumbar switch,
SW Converter for Digital AM Car Radio
20W Bridge Audio Amplifier Wiring diagram Schematic
- 20W Bridge Audio Amplifier kit, based on the TDA2005 IC, a class B dual audio amplifier, specifically designed for car radio applications etc.
- Power supply - 18 VDC
- Output power - 20 W, 4 Ω
- IC built in Thermal Shut-down, Load dump voltage surge protected
- Terminal pins for connecting left and right audio signal inputs
- Relimate Connector for connecting Potentiometer (POT) for volume adjustment
- Power Battery Terminal (PBT) for easy power supply and speaker connection
- Power-On LED indicator
- Heatsink for IC
- Four mounting holes of 3.2 mm each with nut and stud
- PCB dimensions 63 mm x 65 mm
20W Bridge Audio Amplifier Circuit Diagram
Pcb

Parts List

Saturday, September 13, 2014
Samsung will introduce the Galaxy Note 4 on 3 September
It is expected that Samsung present its new phone Samsung Galaxy Note 4 officially in September during IFA 2014 event held in Berlin, Germany. Now, the Korean media already have an exact date of this phone Samsung.
According to The Korea Times, Samsung will be announcing the Galaxy Note 4 on September 3, a day before the presentation of the Galaxy Note 3 last year.
Samsung is expected to start sending invitations to the event "soon", including that the company would be a bit rushed to launch its new mobile big Lcd because Apple is finally breaking its tradition of offering only one size cell relatively small as the iPhone 6 to gain entry to the high-end market. It is said that Samsung is trying to get the Galaxy Note sale 4 days before what went on Galaxy Note 3 with this same purpose.
It is expected that the Samsung Galaxy Note 4 has a QHD (2560 × 1440) 5.7 inch Lcd, a Snapdragon 805 / Exynos 5433 processor, 3GB of RAM and a 16 megapixel camera that would include the Sony IMX240 sensor. Additionally, he said that the Samsung Galaxy Note 4 would an ultraviolet sensor and Android KitKat.
Wheatstone bridge
measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two
legs of a bridge schema, one leg of which includes the
unknown component. Its operation is similar to the original
potentiometer. It was invented by Samuel Hunter Christie in
1833 and improved and popularized by Sir Charles
Wheatstone in 1843. One of the Wheatstone bridges initial
uses was for the purpose of soils analysis and
comparison.

12 Watt Audio Amplifier
This low cost amplifier is simple and give you good result. Here the op-amp used is uA 741 which produces the required gain.The four transistors are wired as complementary Darlington’s which produces the drive for the speaker.
The voltage drop across the resistors R2 and R3, are used as the input of the Darlington pairs . As the input current to the op-amp depends on the level of the signal op amp is amplifying the voltage drop across the resistors R2 and R3 will be proportional to the input signal. These voltage drops are given to the base of Darlington pairs. The amplification is stabilized as a result of the negative feedback from the junction of collectors of Q2 and Q4. The theory may seem little awkward for you. But its working good.cSuch a simple but stable schema as this can produce a reasonable output of 12W on a 4 Ohm speaker.
Friday, September 12, 2014
10 to 14W Class A Audio Amplifier Wiring diagram Schematic
Simple Portable Solar Lantern Wiring diagram Schematic
Simple Portable Solar Lantern Circuit Diagram
DC to AC with NE 555
This is a inverter schema by using this schema you can get 230v current.If your an under age one be careful when you deal with this.Always try to get the assistance of an elder.If there was a fault we cant get the responsibility of it.